Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Extracorporeal Radial and Focus Shock Wave Therapies
In the realm of physiotherapy and rehabilitation, shock wave therapy has emerged as a promising modality for treating various musculoskeletal conditions. Among the different types of shock wave therapy, Extracorporeal Radial and Focus Shock Wave Therapies have gained significant attention for their effectiveness in managing pain and promoting tissue healing. This article delves into the mechanisms of action, applications, and therapeutic benefits of focus and radial shock wave therapies in clinical practice.
Mechanisms of Action
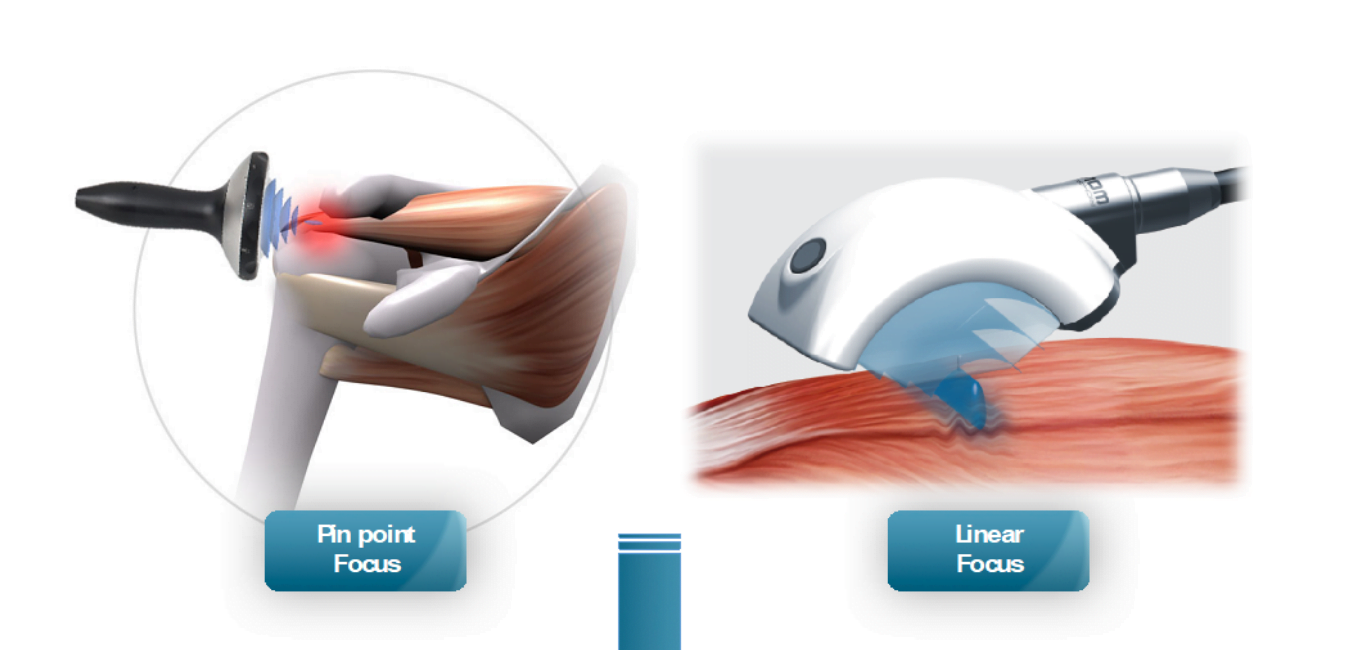
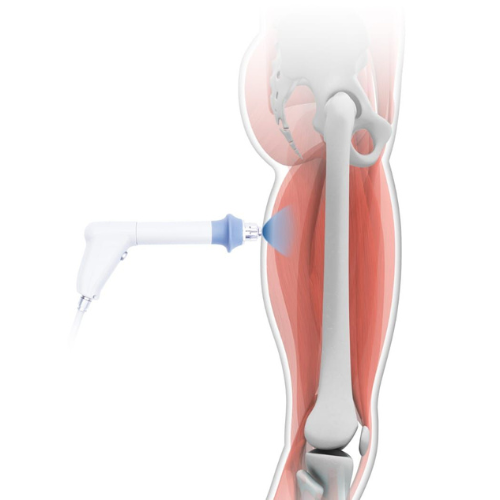
Extracorporeal Radial and Focus Shock Wave Therapies wave therapies exert their therapeutic effects through distinct mechanisms. Focus shock waves are characterized by their high energy density and precise focal point, whereas radial shock waves are low to medium energy waves that spread radially from the applicator. Despite their differences, both modalities induce biological responses within tissues through mechanotnsduction, leading to enhanced tissue regeneration, neovascularization, and modulation of pain pathways. Focus shock waves primarily target deep-seated musculoskeletal structures, whereas radial shock waves are well-suited for treating superficial tissues and trigger points.
Extracorporeal Radial and Focus Shock Wave Therapies is commonly employed for treating chronic conditions such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinopathy, and calcific shoulder tendinitis. Its ability to deliver high-energy waves precisely to the target area makes it particularly effective for deep-seated pathologies. On the other hand, radial shock wave therapy finds applications in conditions like lateral epicondylitis, patellar tendinopathy, and myofascial pain syndromes. Its broader dispersion pattern makes it suitable for treating larger areas and superficial soft tissues.

Applications

Therapeutic Benefits
Both Extracorporeal Radial and Focus Shock Wave Therapies therapies offer several therapeutic benefits. They promote tissue healing by stimulating the release of growth factors and cytokines, which enhance cellular proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis. Moreover, these modalities exert an analgesic effect by modulating pain receptors and reducing inflammation. Unlike surgical interventions, shock wave therapy is non-invasive and typically associated with minimal side effects, making it a preferred choice for patients seeking alternative treatment options.
Clinical Evidence
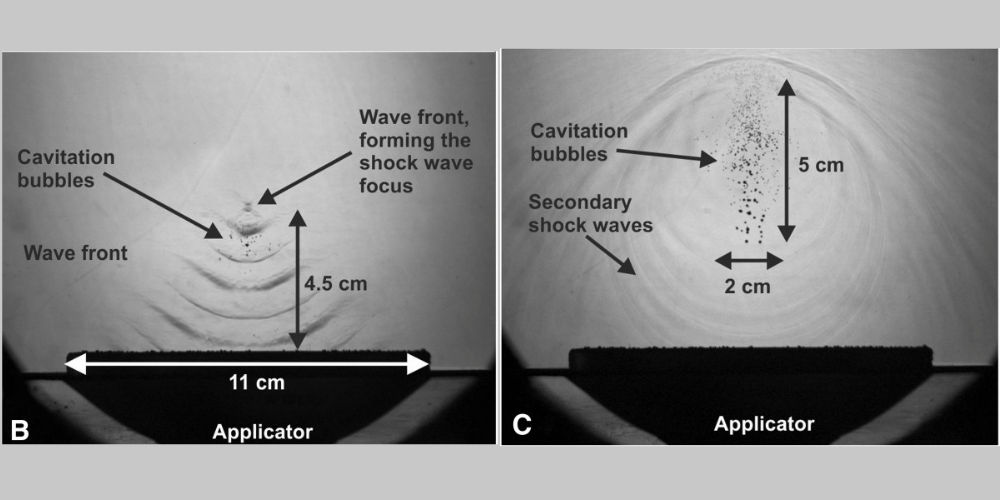
Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Extracorporeal Radial and Focus Shock Wave Therapies across various musculoskeletal conditions. Meta-analyses and systematic reviews have highlighted their superiority over conventional therapies in terms of pain relief, functional improvement, and patient satisfaction. Moreover, the long-term benefits of shock wave therapy, including reduced recurrence rates and improved quality of life, have been well-documented in the literature.
Conclusion:
Extracorporeal Radial and Focus Shock Wave Therapies wave therapies represent valuable additions to the armamentarium of physiotherapists and healthcare providers for managing musculoskeletal disorders. By harnessing the regenerative potential of shock waves, these modalities offer a safe, effective, and non-invasive approach to pain management and tissue repair. Continued research efforts aimed at optimizing treatment protocols and exploring new applications are essential for furthering our understanding of shock wave therapy and maximizing its clinical utility. At our clinic, we offer a range of cutting-edge treatments, including radial and Extracorporeal Radial and Focus Shock Wave Therapies, to address various conditions. From chronic pain to musculoskeletal injuries, our comprehensive approach ensures personalized care tailored to your specific needs. Take control of your health and schedule an appointment with us today to explore the possibilities of effective treatment.
References:
Wang CJ. An overview of shock wave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. Chang Gung Med J. 2003;26(4):220-232.
Furia JP. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for musculoskeletal conditions. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):166.
Speed CA. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the management of chronic soft-tissue conditions. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(2):165-171.
Rompe JD, et al. Repetitive low-energy shock wave application without local anesthesia is more efficient than repetitive low-energy shock wave application with local anesthesia in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(4):931-941.
Leave a Reply
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.

